Teaching math word problems without keywords? Yes, you can! In this blog post, I share how I use operation situations to help with math word problems.
“Who can tell me a word that tells us to add when we solve a word problem?”
Fifteen hands shot into the air, some waving that oh-so-familiar “pick-me” wave.
One by one, students shared their words . . .
“in all”
“all together”
“increase”
“add”
“sum”
“total”
“plus”
“combine”
“join”
“together”
“both”
“Wow! You all came up with an amazing list of words, but what about subtraction? What words signal a subtraction problem?”
The students raised their hands to respond.
“deduct”
“decrease”
“how many more”
“take away”
“how many less”
“less than”
“minus”
“remain”
“difference”
Once the teacher recorded the words on chart paper, the students divided themselves into groups of two and completed a set of addition and subtraction task cards.
—
While the students created an impressive list of words, I wondered if all the students would be able to remember them when solving word problems.
I’m thinking, no! 😕
So, what’s wrong with using math keywords?
An Alternative To Keywords
If we can’t expect students to recognize these signal words to know what to do, how do we help with math word problems?
Great question– I can answer it with two simple words– operation situations.
Now, don’t get me wrong, I have been guilty of expecting my students to pick up on these keywords when solving problems too; however, a conference session I attended many years ago changed my way of thinking.
At the time, I taught fourth grade and dedicated a portion of my math instruction to help my students develop word problem analysis skills with a word problem of the day program.
As we read each day’s word problem, I noticed something interesting . . . each problem fell in a specific category for each operation.
I couldn’t believe it! It was like magic!
In the beginning, I referred to the set of operation situations I learned about at the summer conference session.
They included:
- Addition: part-part-whole, joining
- Subtraction: something leaves; comparing, missing part
- Multiplication: groups of something
- Division: how many groups; how many in each group

Using Operation Situations To Help With Math Word Problems
Each time we encountered a new word problem, I asked the students to describe the event(s) happening in the word problem. From there, we discussed what action (operation) was taking place.
From the beginning, most students could connect the picture they created in their heads with an operation. Then, I helped them connect the situation illustrated in the story problem with the more formal language of the corresponding operation situation.
Example #1
Consider the following problem:
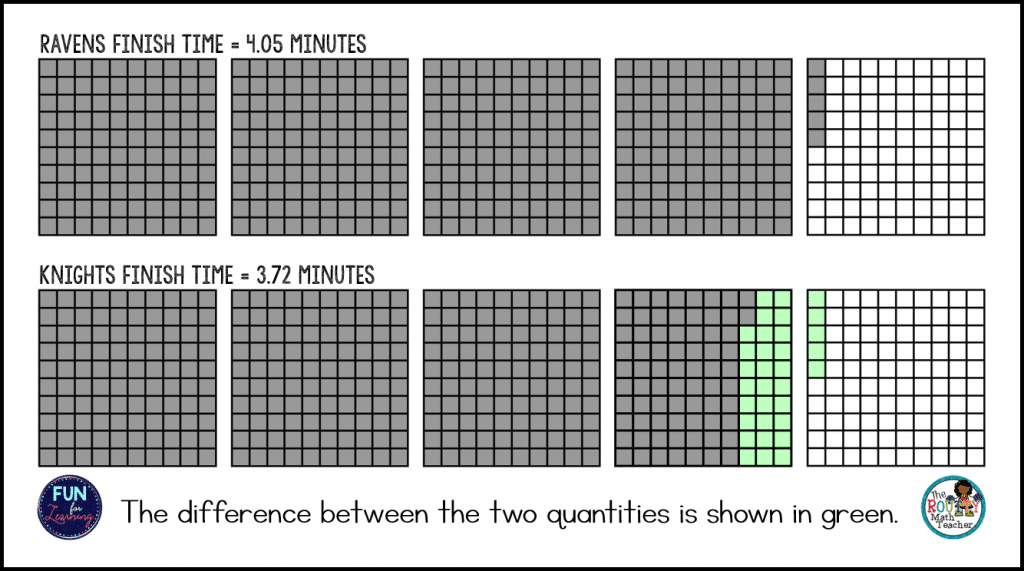
The Lions finished the 400-meter freestyle relay race in 3.83 minutes. The Ravens finished in 3.72 minutes. The Knights finished in 4.05 minutes. What is the difference between the finish times for the first and third place teams?
For this problem, students might say we are looking for the difference between the finish time for the Ravens (first place) and the Knights (third place) relay race team. Students might also say we need to find out how much faster the first-place team (the Ravens) finished the race than the third-place team (the Knights).
During this discussion, if not mentioned by a student, I would add we need to compare the Ravens time to the Knights time and state, “when we compare two numbers, we determine the difference between the two quantities”. I might even follow with a visual to help the students understand what it means to find the difference between two numbers. (See the image below.)
Example #2
Okay. I know what you’re thinking . . . what about multiple-step problems?
That’s a great question. Let’s consider another problem.
When Brandon and Kelly arrive at the BrightStar campground, they begin preparing dessert to eat after their campfire cookout. There are eight people on the camping trip. Brandon and Kelly prepare three smores for each person. Each smore has one marshmallow. If the bag of marshmallows they used had 4 dozen marshmallows, how many marshmallows are leftover?
For this problem, students will call it a subtraction situation because they need to determine the leftover amount. I would revoice their thinking and call this a “something leaves” situation because they started with a bag of 4 dozen marshmallows, then some left, and there is now a specific amount remaining.
The only missing piece of information from this situation is the quantity removed. So we go back to the problem to look for clues.
Looking for Clues
When we return to the problem, we see there are eight people on the camping trip. We also know Brandon and Kelly prepare three smores for each person and each smore has one marshmallow. So, to determine how many marshmallows Brandon and Kelly need, we use the “groups of something” situation– which means to multiply 8 people x 3 smores (marshmallows).
Hopefully, students will also notice the conversion. It’s not necessarily an operation situation we need to flesh out, but students need to acknowledge it. After working through the pieces of information needed to solve the problem, students can articulate they need to subtract the number of marshmallows used (8 groups of 3) from the total in the bag (4 dozen).
Wait . . . there’s a keyword here.
Right now, you might be saying to yourself, “This problem has a keyword, so why is all of this necessary?”
Because, this problem could have been written without the use of the word “leftover.” In fact, it could say, “If the bag of marshmallows they used had 4 dozen marshmallows, how many marshmallows were in the bag when Brandon and Kelly put the supplies away after dessert.” Notice there isn’t a keyword here, so some students might feel discouraged before even starting.
The Bottom Line
We want our students to engage with story problems so they can see the story in their heads. Can you see Brandon, Kelly, Brenda, Dylan, Andrea, Steve, Donna, and David around the campfire after their high school graduation making smores? (Yes, you guessed it . . . I’m an 80s child and loved watching 90210!)
When students can visualize the situation, they can make sense of the actions taking place, such as someone counting the number of marshmallows they need and removing them from the bag. After recognizing the action, we can easily determine the quantity remaining.
More Operation Situations
I’m sure you’re wondering how I went from eight situations to the seventeen situations on the operation situations printable I shared in my keywords for math problems blog post.
During the first year I used this strategy to help my students with math word problems, my students and I noticed some situations didn’t quite fit, such as money situations where we know the amount spent and the change received but need to know the amount given to the cashier.
These types of problems made me curious to look for more situations I could use to address all of the types of problems we encountered; however, these initial eight situations were a great starting place and helped my students become proficient at solving math word problems for a great number of years.
Ready to use the operation situations to help with math word problems? Download a free set of posters using the form below!
Sound Off!
What strategies do you use to help with math word problems? Respond in the comments below.






3 Responses
I appreciate this resource – and was led here via your email subscription. To get this resource, am I subscribing a second time to the same blog post emails? I’m confused.
Hi Manda!
Great question! No, you are not subscribing a second time, but the system will tag you to show you downloaded the resource. That helps me know what our teacher community wants to know more about. Nothing will change in terms of the emails– you won’t receive double the number. I hope this helps. If you have any other questions, please email me at [email protected]. Thank you!
~ Shametria
I am a teacher of students with visual impairments & am working with a 4th grade student (braille reader) who struggles with determining what operations are needed in word problems – esp. those doozies that require doing two. I am excited to take a different approach. I don’t want to spend valuable time teaching him operation words when I could be teaching him how to think more holistically. Generalization is often a problem for these students because they have such limited experience. Thank you for sharing your teaching knowledge.